How Does an Antistatic Floor Work? Everything You Need to Know About This Smart Flooring Solution
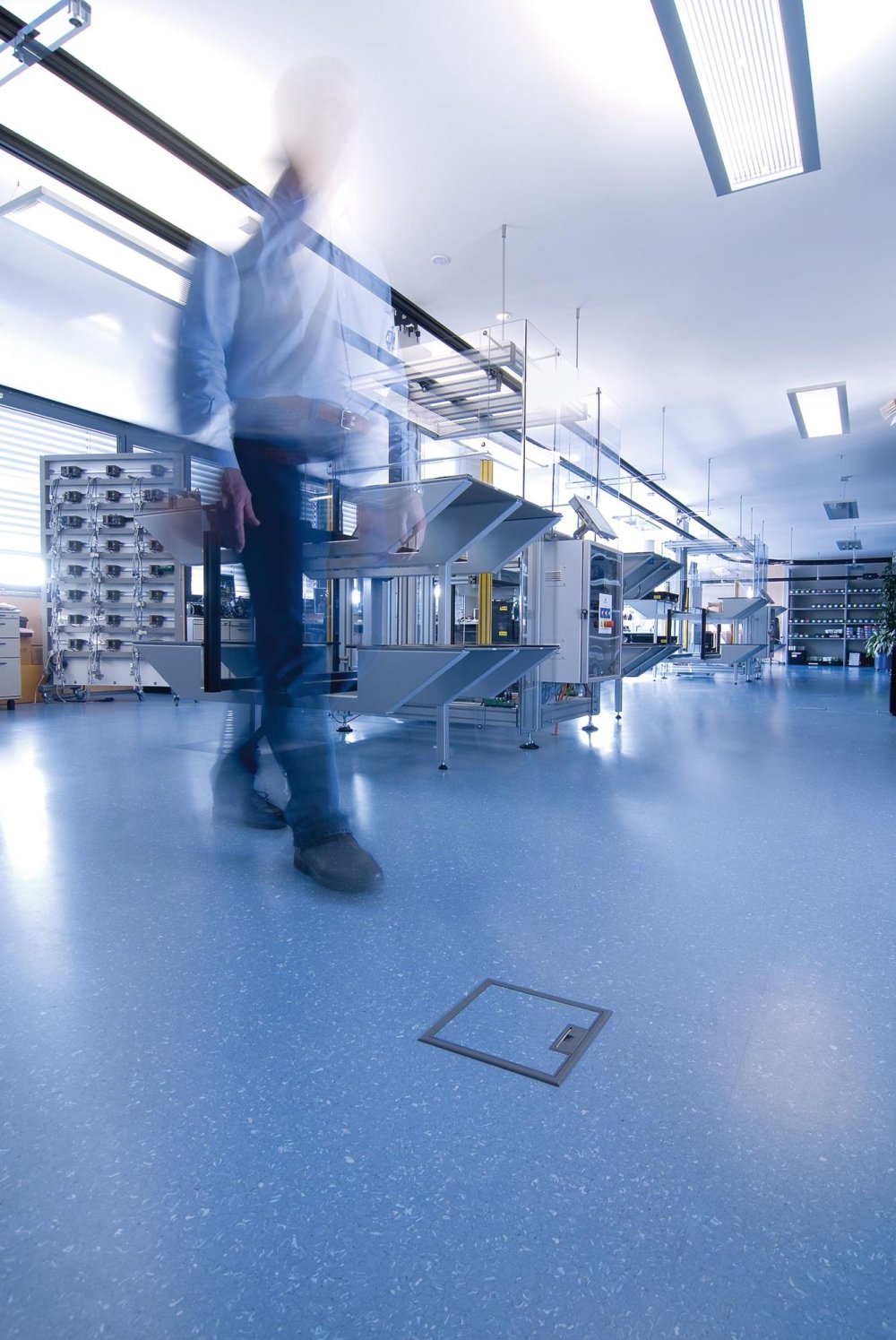
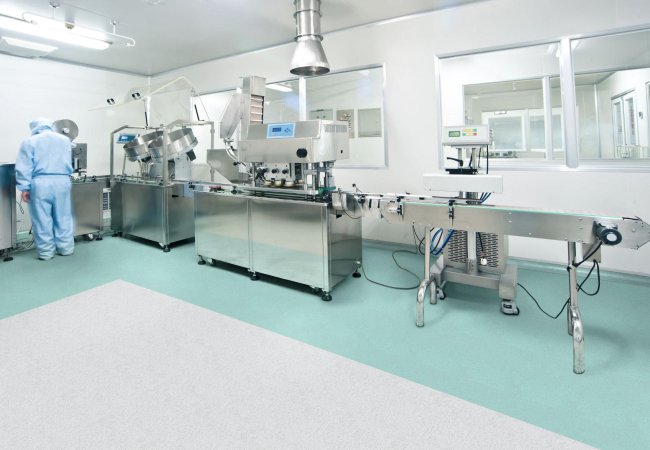
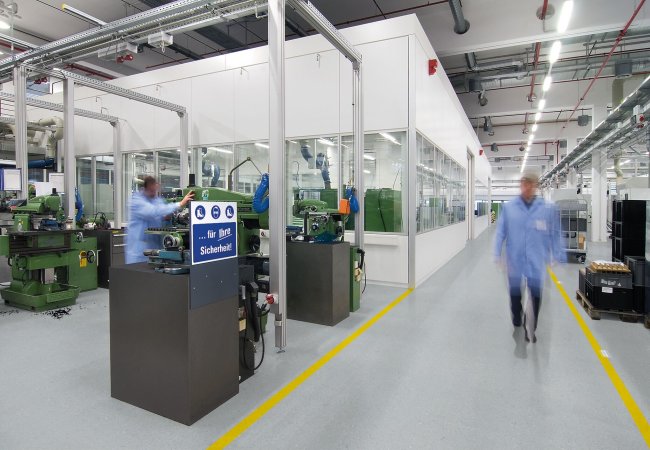
In certain environments, controlling electrostatic discharge (ESD) is absolutely essential. Laboratories, clean rooms, and EPA zones (Electrostatic Protected Areas) require specialized floor coverings that can safely manage and dissipate static electricity. These floors protect equipment, sensitive components, and personnel from risks associated with electrostatic charges.
What is ESD?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden transfer of static electricity between two objects at different electrical potentials. While usually harmless in daily life, in technical environments it can:
- damage sensitive electronic components,
- disrupt measurement instruments,
- compromise the safety of clean rooms or laboratories.
That’s why specialized flooring — conductive or dissipative — is installed to ensure effective grounding.
Conductive floors
Conductive floors are designed to redirect electrostatic charges quickly and directly to ground. They are highly effective and used in the most sensitive environments.
To illustrate: using a sports-field analogy, the ball representing the static charge travels straight into the goal — the ground.
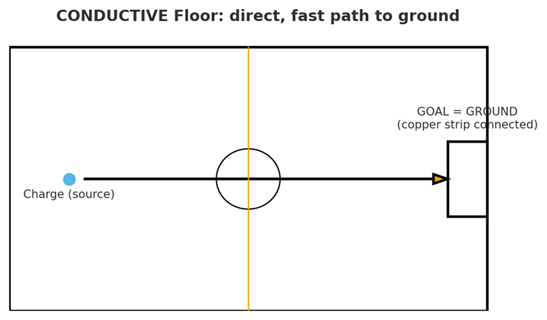
How it works:
- the flooring contains conductive elements (carbon flakes, fibers, or special layers);
- these are connected with conductive adhesive or integrated directly into the material;
- a copper foil strip is installed beneath the floor and connected to the building ground;
- this creates a direct path for charges to flow.
Dissipative floors
Dissipative floors work differently. Instead of evacuating charges instantly, they dissipate them gradually, preventing abrupt discharges while maintaining safe control.
With the same sports-field analogy, the ball (the charge) makes several successive passes between players before reaching the goal (the ground).
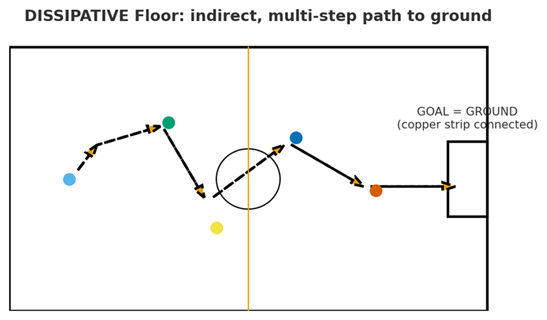
How it works:
- the flooring contains dissipative materials, sometimes in the adhesive, sometimes within the product itself;
- charges move slowly toward the grounding point;
- the copper foil strip ensures continuity so all charges are directed to ground.
Why correct installation matters
Whether the floor is conductive or dissipative, installation is critical:
- use conductive adhesive or integrated conductive particles,
- install copper foil strips beneath the flooring,
- make a final connection to the outlet’s grounding system.
Where are these floors used?
Anti-static and ESD flooring is essential in:
- laboratories with sensitive equipment,
- clean rooms, where even small disturbances compromise operations,
- EPA zones, where controlled evacuation of electrostatic charges is strictly required.






